Fatty acids
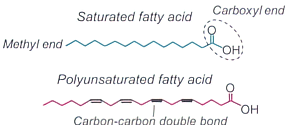
Fatty acids consist of a hydrocarbon chain of varying length (typically 14 to 26 carbon atoms) and degrees of unsaturation (typically 0 to 6 double bonds). Fatty acids contain a methyl group at one end (the omega end) and a carboxyl group at the other end. The general nomenclature used to describe fatty acids is XX:Y where XX indicates the number of the carbons in the acyl chain and Y denotes the number of double bonds within the hydrocarbon chain. For example, the fatty acid shown in pink is arachidonic acid (20:4), a poly-unsaturated fatty acid with a 20 carbon atom long acyl chain that contains 4 double bonds. Note that the first double bond from the omega end is at the 6th carbon atom, indicating that this is an omega-6 fatty acid. In omega-3 fatty acids the first double bod comes at the 3rd carbon atom. Differences in chain length and saturation status (number, position and orientation of double bonds) alters the biochemical and biophysical properties of fatty acids and, consequently, the complex lipids that they are components of (described below).
Glycerophospholipids
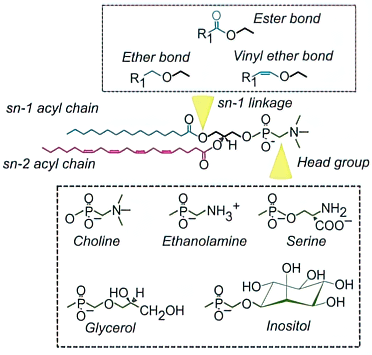
Glycerophospholipids (PL) are the major lipid constituent of cell membranes. PLs contain a glycerol backbone and are typically either di-acylated (i.e. they contain 2 fatty acid-derived acyl chains) or are alkylated/acylated (i.e. they contain a fatty alcohol-derived alkyl chain and a fatty acyl chain [such lipid are termed ether-lipids]). A phosphate-containing polar headgroup is the final component of PL. Depending on the variable phosphorylated headgroup, phospholipids can exist as either phosphocholine (PC), phosphoethanolamine (PE), phosphoserine (PS), phosphoglycerol (PG) and phosphoinositol (PI). The combination of the above described variations in PL structure is the basis for the complexity of the glycerophospholipidome and underpins the many distinct functional properties of different lipid classes and lipid species.
Sphingolipids
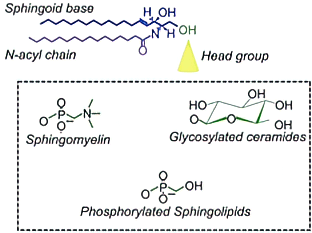
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids with roles in membrane integrity and cellular signalling, all characterised by the presence of a sphingoid base backbone. At the centre of sphingolipid metabolism is the bioactive intermediate ceramide (Cer), which consists of an acyl chain linked to the sphingoid base. Ceramide can be metabolised into complex sphingolipids such as sphingomyelin (SM), hexosylceramides (HexCer) and gangliosides (GM).
Cholesterol
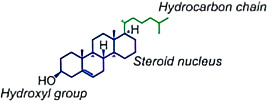
Cholesterol is a type of sterol that is synthesised from acetyl-CoA incorporation into the mevalonate pathway. Within the lipid bilayer, they function to maintain membrane fluidity.
Lipid abbreviations
| Class Name | Abbreviations |
|---|---|
| Dihydroceramide | dhCer |
| Ceramide | Cer(d) |
| Deoxyceramide | Cer(m) |
| Monohexosylceramide | HexCer |
| Dihexosylceramide | Hex2Cer |
| Trihexosylceramide | Hex3Cer |
| GM3 ganglioside | GM1 |
| GM1 ganglioside | GM3 |
| Sphingomyelin | SM |
| Phosphatidic acid | PA |
| Phosphatidylcholine | PC |
| Alkylphosphatidylcholine | PC(O) |
| Alkenylphosphatidylcholine | PC(P) |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine | LPC |
| Lysoalkylphosphatidylcholine | LPC(O) |
| Lysoalkenylphosphatidylcholine | LPC(P) |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine | PE |
| Alkylphosphatidylethanolamine | PE(O) |
| Alkenylphosphatidylethanolamine | PE(P) |
| Lysophosphatidylethanolamine | LPE |
| Lysoalkenylphosphatidylethanolamine | LPE(P) |
| Phosphatidylinositol | PI |
| Phosphatidylinositol monophosphate | PIP1 |
| Lysophosphatidylinositol | LPI |
| Phosphatidylserine | PS |
| Lysophosphatidylserine | LPS |
| Phosphatidylglycerol | PG |
| Cholesterol | COH |
Cell markers
Cell surface markers used to purify the different cell populations
Human
| Cell | Surface marker |
|---|---|
| Naïve B cell | CD19+ CD27+ Mitotracker- |
| Memory B cell | CD19+ CD27+ Mitotracker+ |
| CD4 Naïve T cell | CD3+ CD4+ CCR7+ CD45RA+ |
| CD4 Central Memory T cell | CD3+ CD4+ CCR7+ CD45RA- |
| CD4 Effector Memory T cell | CD3+ CD4+ CCR7- CD45RA- |
| CD8 Naïve T cell | CD3+ CD8+ CCR7+ CD45RA+ |
| CD8 Central Memory T cell | CD3+ CD8+ CCR7+ CD45RA- |
| CD8 Effector Memory T cell | CD3+ CD8+ CCR7- CD45RA- |
| CD56 Dim Natural Killer cell | CD3- CD56+ CD16- |
| CD56 Bright Natural Killer cell | CD3- CD56+ CD16+ |
| Classical Monocyte | Lin- HLA-DR+ CD14+ CD16- |
| Intermediate Monocyte | Lin- HLA-DR+ CD14+ CD16+ |
| Non-classical Monocyte | Lin- HLA-DR+ CD14dim CD16- |
| Basophil | HLA-DR- CD203c+CD123+ |
| Eosinophil | SSChigh Siglec8+ |
| Neutrophil | SSChigh CD15+ CD16+ |
Mouse
| Cell | Surface marker |
|---|---|
| B cells | CD45+ CD3- CD19+ |
| Natural Killer cells | CD45+ CD3- NK1.1+ |
| CD4 T cells | CD45+ CD3+ CD4+ |
| CD8 T cells | CD45+ CD3+ CD8+ |
| Ly6Clo monocytes | CD45+ CD115+ Gr1- |
| Ly6Chi monocytes | CD45+ CD115+ Gr1+ |
| Neutrophils | CD45+ CD115- Gr1+ |
| Eosinophils | CD45+ SSChigh SiglecF+ |